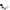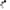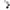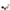The D30V3x line of synchronous buck (step-down) voltage regulators generates lower output voltages from input voltages as high as 45 V. They are switching regulators (also called switched-mode power supplies (SMPS) or DC-to-DC converters), which makes them much more efficient than linear voltage regulators, especially when the difference between the input and output voltage is large. These regulators can typically support continuous output currents between 1 A and 4 A, depending on the input voltage and output voltage. In general, the available output current decreases as the input and output voltages increase.

D30V3x line of step-down voltage regulators. From left to right: D30V30Fx, D30V30MASx, D30V33MASx.
This line consists of the D30V30Fx family of fixed output voltages ranging from 3.3 V to 15 V and two families of adjustable versions that allow the output voltage to be set with a precision 11-turn potentiometer. Each adjustable option is available with or without an adjustable low-voltage cutoff (also set through a precision 11-turn potentiometer on the versions that have it). The adjustable families are the D30V30MAx, which is the more compact of the two thanks to its double-sided assembly, and the D30V33MAx, which includes larger through-holes for terminal blocks and can do slightly more current thanks to its larger surface area. The following table shows all of the members of the D30V3x line:
The regulators have reverse voltage protection up to 40 V, input under-voltage lockout, over-current protection, and short-circuit protection. A thermal shutdown feature also helps prevent damage from overheating and a soft-start feature limits the inrush current and gradually ramps the output voltage on startup.
If you need higher input voltages, consider the similar D36V28Fx family, which works up to 50 V in, and if you need more output current, consider the similar D36V50Fx family of step-down voltage regulators.
Details for item #4855:
This item is the D30V33MAS, which has an adjustable output voltage (4.2 V to 15 V) and no low-voltage cutoff (see the D30V33MASCMA for a version of this regulator with an adjustable low-voltage cutoff):

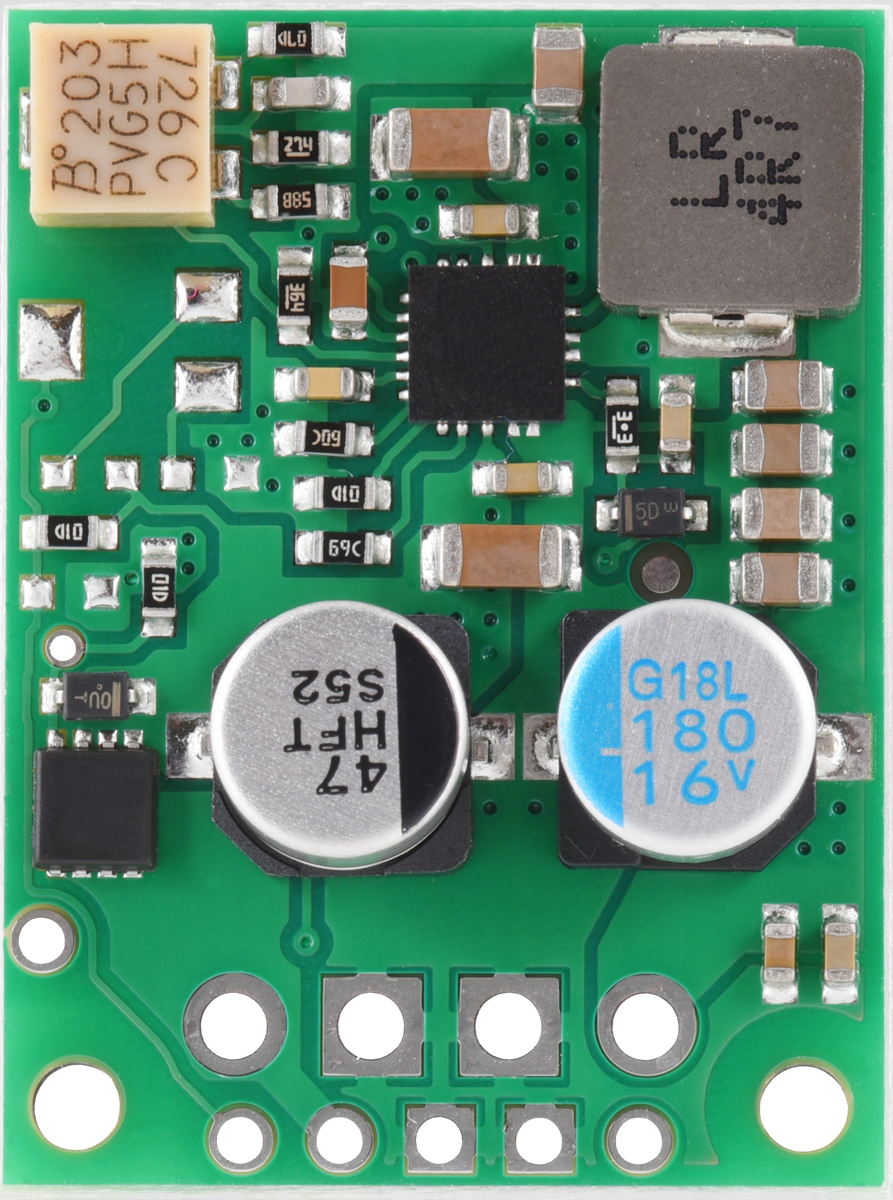

Features:
- Input voltage: VOUT to 45 V (input must be higher than the output voltage and is subject to dropout voltage considerations; see the dropout voltage section for details)
- Output voltage: 4.2 V to 15 V (precision-adjustable using built-in 11-turn potentiometer)
- Typical maximum continuous output current: 1.3 A to 4.3 A (see the maximum continuous output current graph below)
- Typical efficiency of 80% to 95%, depending on input voltage, output voltage, and load (see the efficiency graphs below)
- Very low dropout voltage
- Switching frequency: ~700 kHz under heavy loads
- Power-save mode that increases light load efficiency by reducing switching frequency
- Low quiescent current (see the quiescent current graph below)
- Enable input with precise cutoff threshold for disconnecting the load and putting the regulator into a low-power shutdown state that draws approximately 10 µA to 20 µA per volt on VIN
- “Power good” output indicates when the regulator cannot adequately maintain the output voltage
- Frequency spread spectrum operation that lowers peak EMI noise
- Under-voltage lockout protection
- Soft-start feature limits inrush current and gradually ramps output voltage
- Integrated reverse-voltage protection up to 40 V, over-current and short-circuit protection, over-temperature shutoff
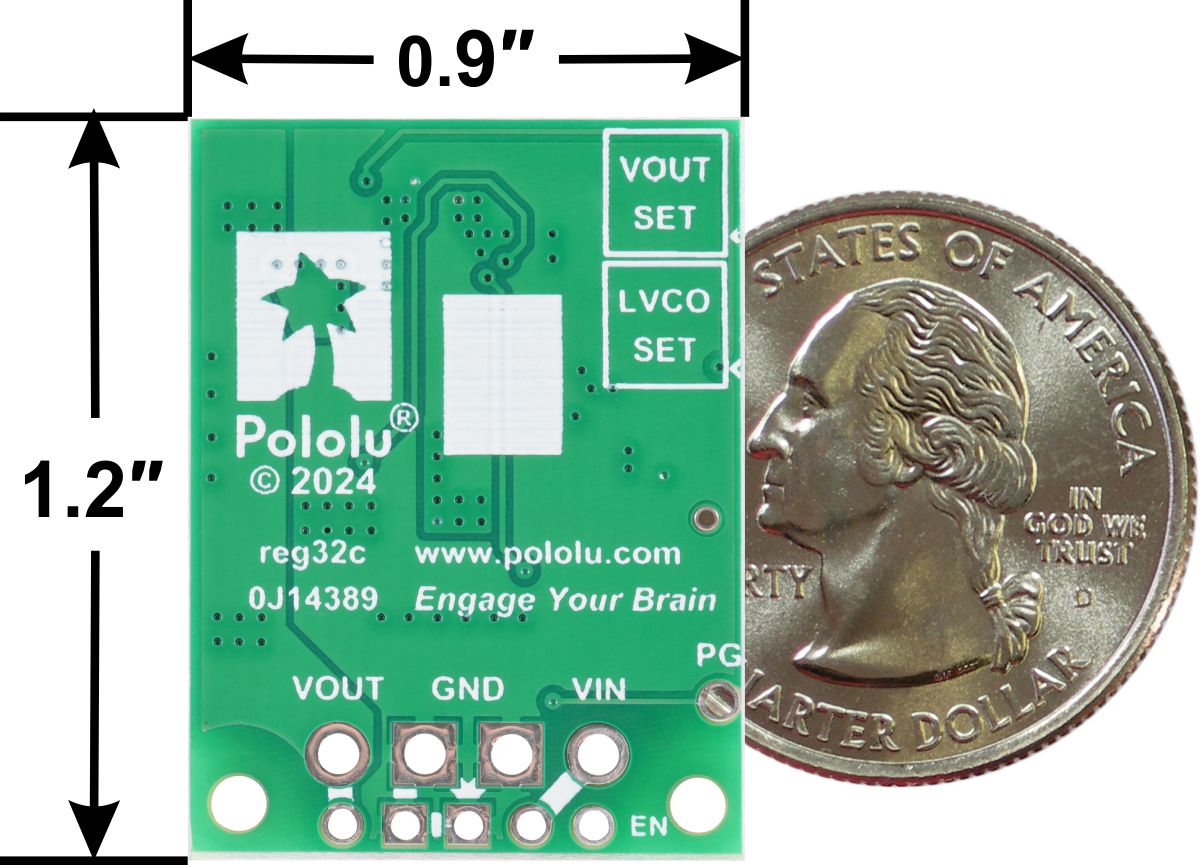
- Size: 0.9″ × 1.2″ × 0.3″ (22.9 mm × 30.5 mm × 7.7 mm); see the dimension diagram (306k pdf) for more information
- Two 0.086″ mounting holes for #2 or M2 screws
- Through-holes for 0.1″ headers as well as for 3.5mm-pitch terminal blocks
Using the Regulator
Connections
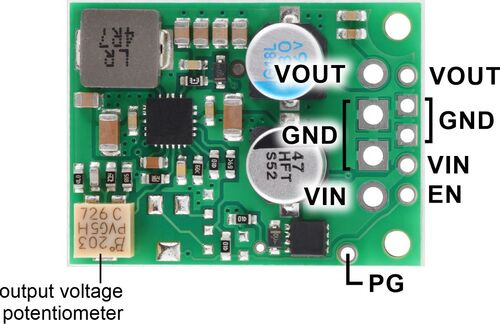
This regulator has six connections: power good (PG), enable (EN), input voltage (VIN), output voltage (VOUT), and two ground (GND) connections.
The “power good” indicator, PG, is an open-drain output that goes low when the regulator’s output voltage either rises more than 7.5% (typical) above or falls more than 9% (typical) below the voltage it is trying to maintain (with hysteresis). An external pull-up resistor is required to use this pin.
The regulator, which is enabled by default, can be put into a low-power sleep state by reducing the voltage on the EN pin below 0.85 V (typical; the actual threshold can vary between 0.65 V and 1.05 V from unit to unit), and it can be brought out of this state again by increasing the voltage on EN past 1 V (typical). The shutdown current draw in this sleep mode is dominated by the current in the 100 kΩ pull-up resistor from EN to VIN and in the reverse-voltage protection circuit, which altogether will be between 10 µA and 20 µA per volt on VIN. (Note that for high input voltages, the shutdown current draw when it is disabled can be greater than the quiescent draw while enabled; see the quiescent current graph below for more details.)
A low-voltage cutoff can be set by adding an appropriately sized external pull-down resistor between EN and GND. This resistor and the on-board 100 kΩ pull-up would together form a VIN voltage divider with the output connected to EN. We also have a version of this regulator with an adjustable low-voltage cutoff built-in.
The input voltage, VIN, powers the regulator. Voltages between 3.3 V and 45 V can be applied to VIN, but generally the effective lower limit of VIN is VOUT plus the regulator’s dropout voltage, which varies approximately linearly with the load (see below for graphs of the dropout voltage as a function of the load).
VOUT is the regulated output voltage, which can be set between 4.2 V and 15 V with the output voltage adjustment potentiometer.
Setting the output voltage
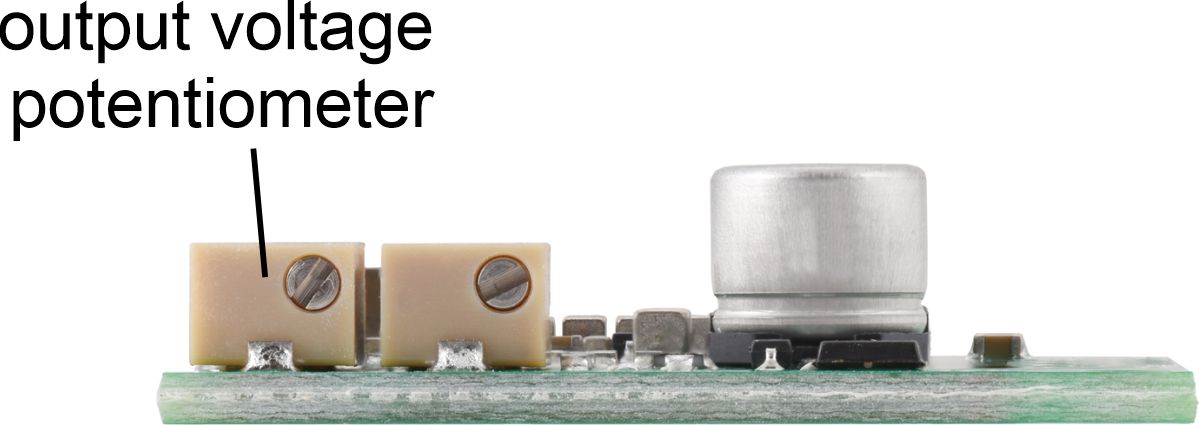
The output voltage is controlled with an 11-turn precision potentiometer that allows for an output range of 4.2 V and 15 V. Turning the potentiometer clockwise increases the output voltage. The regulator ships with a the voltage set to approximately 5 V by default.
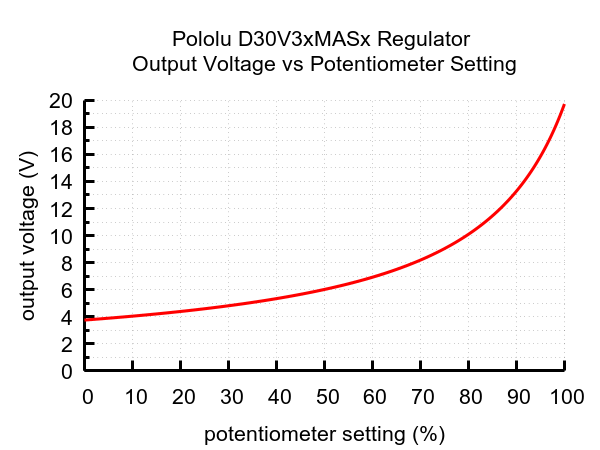
Warning: The output voltage adjustment range allows for voltages over 15 V, but these should not be used. Doing so could result in derated performance or damage to the regulator.
Included hardware:
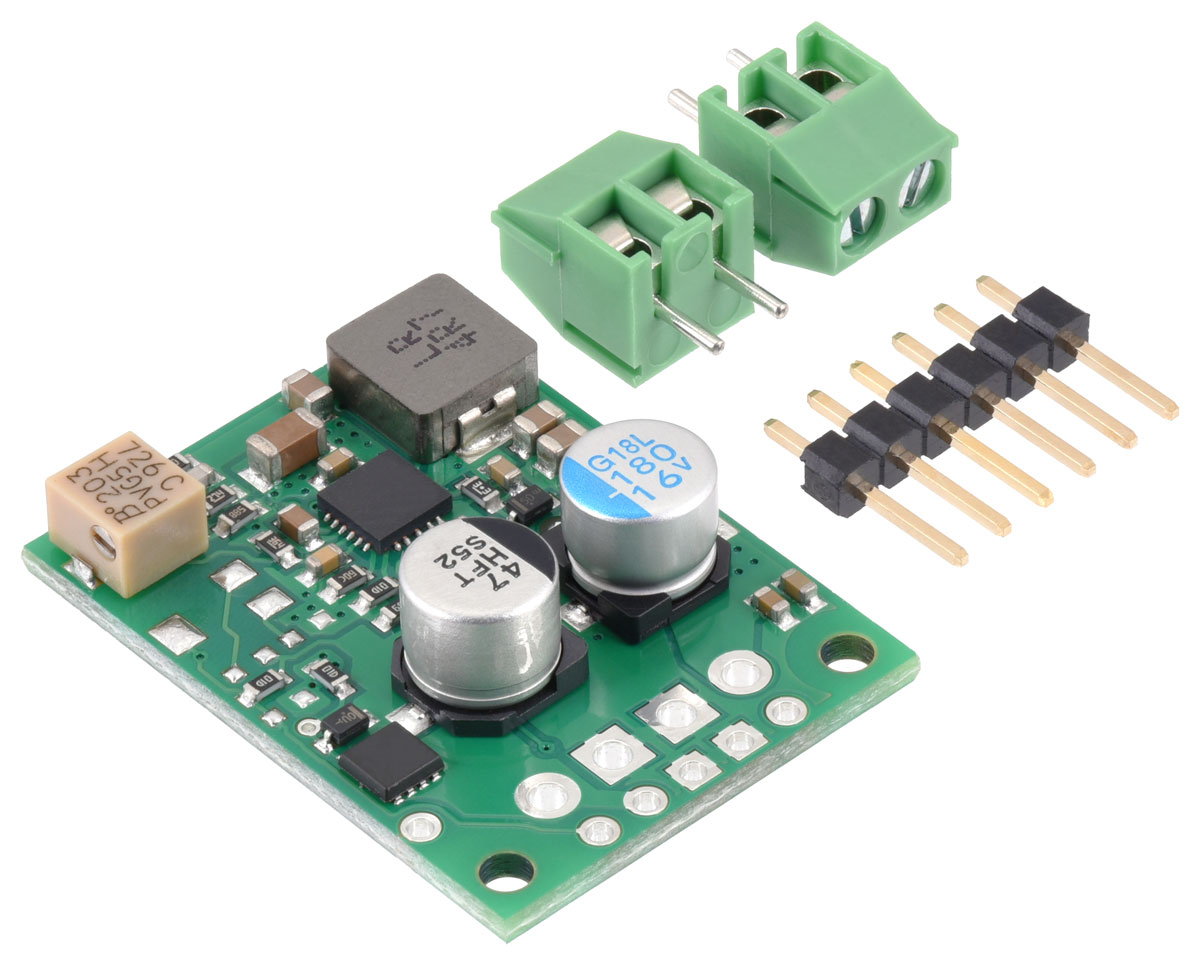
The regulator includes a 6×1 straight male header strip and two 2-pin, 3.5 mm-pitch terminal blocks, and it can be assembled with either the header or terminal blocks. The 0.1″ male header can be soldered into the smaller through-holes, which are arranged on a 0.1″ grid for compatibility with solderless breadboards, connectors, and other prototyping arrangements that use a 0.1″ grid. The PG connection is the only one not located in line with the rest; one pin from the male header strip can optionally be separated with a pair of flush cutters and soldered into PG.
Alternatively, the terminal blocks can be locked together and soldered into the larger holes to allow for convenient temporary connections of unterminated wires (see our short video on terminal block installation). Note: these larger holes only allow for terminal block connections to VIN, VOUT, and GND, not EN or PG. You can also solder wires directly to the board for the most compact installation.
The following pictures show some examples of how these included connectors can be assembled on the regulator (D30V33MASCMA version pictured):
Typical efficiency:
The efficiency of a voltage regulator, defined as (Power out)/(Power in), is an important measure of its performance, especially when battery life or heat are concerns.
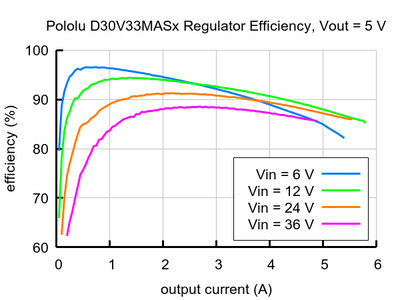
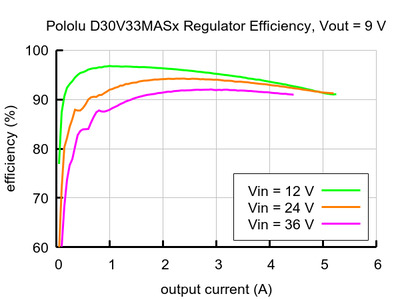
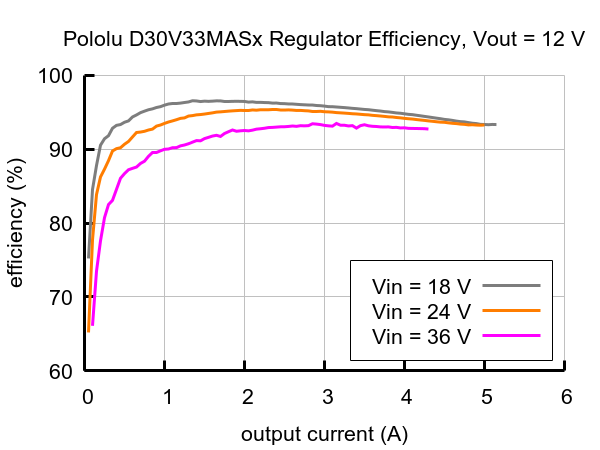
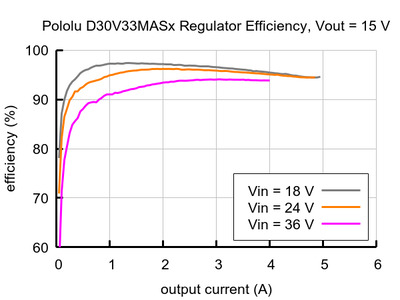
Maximum continuous output current
The maximum achievable output current of these regulators varies with the input voltage but also depends on other factors, including the ambient temperature, air flow, and heat sinking. The graph below shows maximum output currents that these regulators can deliver continuously at room temperature in still air and without additional heat sinking.
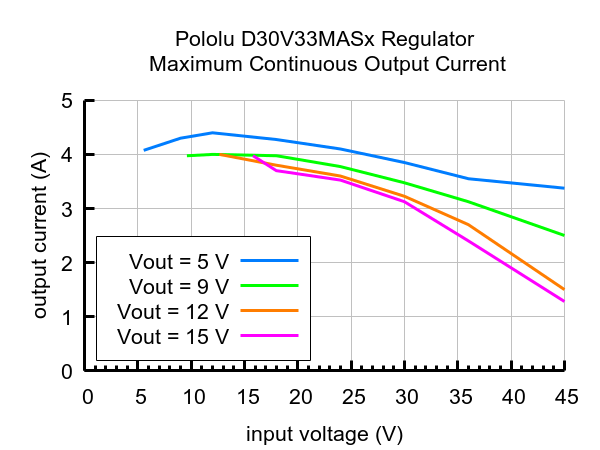
During normal operation, this product can get hot enough to burn you. Take care when handling this product or other components connected to it.
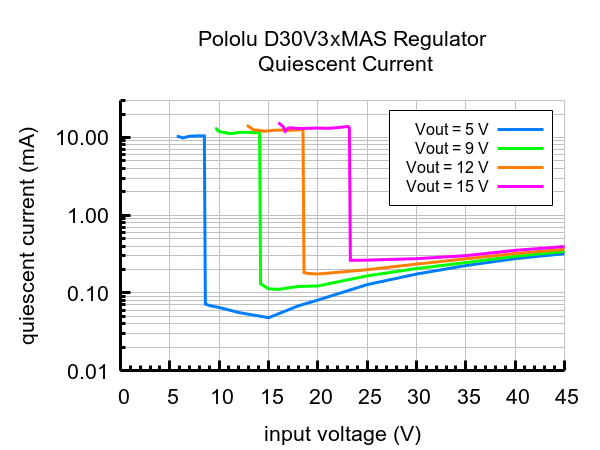
Quiescent current
The quiescent current is the current the regulator uses just to power itself, and the graph below shows this for the different regulator versions as a function of the input voltage.
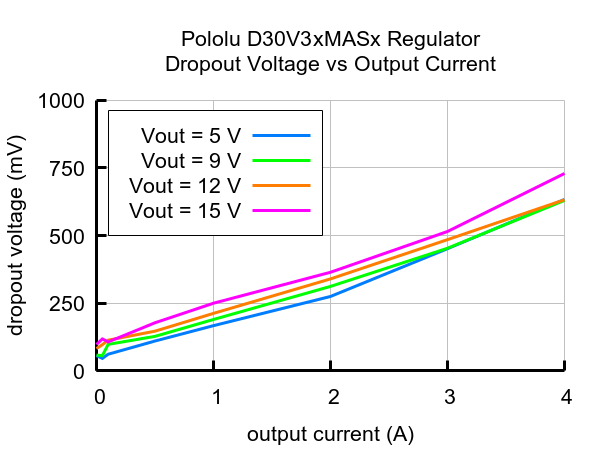
Typical dropout voltage
The dropout voltage of a step-down regulator is the minimum amount by which the input voltage must exceed the regulator’s target output voltage in order to ensure the target output can be achieved. For example, if a 5 V regulator has a 1 V dropout voltage, the input must be at least 6 V to ensure the output is the full 5 V. Generally speaking, the dropout voltage increases as the output current increases. The graph below shows the dropout voltages at several different output voltages as a function of output current:
Package Includes:
- 1 x Pololu 4855 4.2-15V, 3.3A Fine-Adjust Step-Down Voltage Regulator D30V33MAS
Pololu 4855 4.2-15V, 3.3A Fine-Adjust Step-Down Voltage Regulator D30V33MAS
- Brand: Pololu
- Product Code: Pololu-4855-D30V33MAS
- Reward Points: 14
- Availability: In Stock
- रo 1,417.00
-
रo 1,361.00
- Price in reward points: 1417
-
- 10 or more रo 1,406.00
- 25 or more रo 1,344.00
- 52 or more रo 1,333.00
- 96 or more रo 1,283.00
Related Products
Pololu 4082 5V Step-Up/Step-Down Voltage Regulator S13V30F5
This powerful synchronous switching step-up/step-down regulator efficiently produces 5 V from input ..
रo 1,209.00 रo 1,259.00
Pololu 4980/4981/4982/4983/4984/4985 3.3V/6V/7.5V/9V/12V/15V 2.5A Step-Up/Step-Down Voltage Regulator S13V25F3/F6/F7/F9/F12/F15
This synchronous switching step-up/step-down regulator efficiently produces 3.3 V / 6 V / 7.5 ..
रo 1,286.00 रo 1,339.00
Pololu 4891/4892/4893/4894/4895/4896/4897 3.3V/5V/6V/7.5V/9V/12V/15V Step-Down Voltage Regulator D30V30F3/F5/F6/F7/F9/F12/F15
The D30V30Fx family of buck (step-down) voltage regulators generates lower output voltages from inpu..
रo 1,209.00 रo 1,259.00
Pololu 4854 4.2-15V, 3.3A Fine-Adjust Step-Down Voltage Regulator w/ Adjustable Low-Voltage Cutoff D30V33MASCMA
The D30V3x line of synchronous buck (step-down) voltage regulators generates lower output voltages f..
रo 2,271.00 रo 2,365.00
Pololu 4875 4.2-15V, 3A Fine-Adjust Step-Down Voltage Regulator D30V30MAS
The D30V3x line of synchronous buck (step-down) voltage regulators generates lower output voltages f..
रo 1,664.00 रo 1,733.00
Pololu 4874 4.2-15V, 3A Fine-Adjust Step-Down Voltage Regulator w/ Adjustable Low-Voltage Cutoff D30V30MASCMA
The D30V3x line of synchronous buck (step-down) voltage regulators generates lower output voltages f..
रo 1,967.00 रo 2,049.00
Pololu 4852 1.4-7V, 3.8A Fine-Adjust Step-Down Voltage Regulator w/ Adjustable Low-Voltage Cutoff D30V33MALCMA
The D30V3x line of synchronous buck (step-down) voltage regulators generates lower output voltages f..
रo 2,271.00 रo 2,365.00
Tags: Pololu, Fine-Adjust, Step-Down, Voltage, Regulator